Sinus infections and ear infections are common conditions that can cause similar and sometimes overlapping symptoms, making it challenging to distinguish between them. Even though both kinds of infections can, unfortunately, cause discomfort and pain, a proper diagnosis and treatment plan can put you on the right path to recovery.
Keep reading to learn more about the distinctions between sinus infections and ear infections, tips on how to treat them, and what steps you can take to avoid them altogether.
What Is a Sinus Infection?
The sinuses are the air-filled spaces in the skull that surround the nose and eyes, and inflammation of the sinuses is referred to as a sinus infection. A sinus infection is also referred to as “sinusitis”. These infections are the result of viruses, bacteria, or fungi and can be quite uncomfortable. They can also last for several weeks if left untreated. A sinus infection commonly exhibits the following symptoms:
- Facial pressure and pain: You may experience pressure or pain around your forehead, eyes, and nose.
- Nasal congestion: Your nasal passages may be blocked due to inflammation of the sinuses, making it difficult to breathe through the nose.
- Postnasal drip: Sinus infections can cause excess mucus production, which can lead to postnasal drip. This is when mucus drains down the back of your throat, leading to a sore throat, coughing, or a hoarse voice.
- Headache: You may feel a dull or throbbing headache in the front of the head, around the eyes, or in the cheeks.
- Cough: You may develop a cough that is worse at night.
- Fever: You may have a low-grade fever.
- Fatigue: Sinus infections can cause fatigue and a general feeling of being unwell, but sleeping may also be difficult.
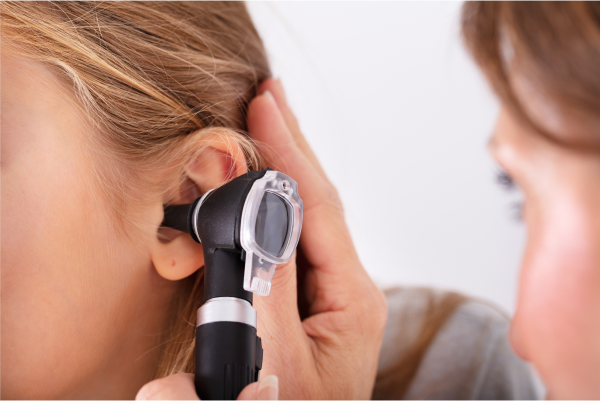
What Is an Ear Infection?
Otitis media, another name for an ear infection, is caused by inflammation of the middle ear. The middle ear is also home to the tiny bones responsible for transmitting sound vibrations. Ear infections are most common in children, but they can affect people of any age. The following are typical signs of an ear infection:
- Ear pain: Ear infections typically cause pain in one or both ears. The pain can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by a feeling of pressure.
- Hearing loss: You may experience a temporary loss of hearing due to the buildup of fluid in the middle ear.
- Ear drainage: If the eardrum ruptures, pus or fluid may leak out of the ear.
- Fever: Ear infections can sometimes cause a low-grade fever.
- Difficulty sleeping: Ear pain may make it difficult to sleep at night.
How to Tell the Difference Between a Sinus Infection and an Ear Infection
While sinus infections and ear infections share some common symptoms, there are a few key differences that can help you tell them apart.
- Location of the pain: Sinus infections typically cause pain and pressure around the nose, eyes, and forehead, while ear infections typically cause pain in one or both ears.
- Nature of the pain: Sinus infection pain is often described as a dull ache, while ear infection pain is often described as a sharp or stabbing sensation.
- Other symptoms: For example, sinus infections often cause nasal congestion, postnasal drip, and headaches, while ear infections often cause hearing loss and ear drainage.
By honing in on your specific symptoms, it should be easier to properly distinguish between sinus infections and ear infections. However, it’s also important to note that some people may experience both types of infections at the same time. This can be especially true if the infection spreads from the sinuses to the ears.
If you’re unsure about the type of infection you have, it’s best to seek medical advice from a healthcare professional, such as your primary doctor or ENT, for an accurate diagnosis.
Tips for Treating a Sinus Infection
Sinus infections can sometimes be treated with home remedies and over-the-counter medications. Here are some things you can do to help alleviate your symptoms:
- Use a humidifier: Humidifiers can help moisten the air, making it easier to breathe.
- Drink plenty of fluids: Staying hydrated can help thin out mucus and reduce congestion.
- Use saline nasal spray: Saline nasal sprays can help clear nasal passages and reduce inflammation.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve facial pain and headaches.
- Rest: Getting plenty of rest can help your body fight off the infection.
If your symptoms persist for more than a week or if you develop a high fever, you should see a doctor. In some cases, antibiotics may be needed to treat a bacterial sinus infection.
Tips for Treating an Ear Infection
If you suspect you have an ear infection, it’s generally advisable to see a doctor sooner rather than later, especially if you are experiencing severe pain or hearing loss. Your doctor will examine your ear and may recommend one or more of the following treatments:
- Antibiotics: If the ear infection is caused by bacteria, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the infection.
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve ear pain.
- Warm compress: Placing a slightly warm compress over the ear can help lessen swelling and make you more comfortable.
- Rest: Resting and avoiding strenuous activity can help your body fight off the infection.
In some cases, an ear infection may cause a ruptured eardrum. If this occurs, your doctor will likely recommend additional treatments to help the eardrum heal.
Preventing Sinus and Ear Infections
While it’s not always possible to prevent sinus and ear infections, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly, especially before eating or touching your face.
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick: If you are around someone who is sick, try to maintain a safe distance.
- Consider vaccinations: Talk to your doctor about which vaccinations have been shown to help prevent ear infections and whether they might be right for you.
- Manage allergies: If you have allergies, take steps to manage your symptoms to reduce your risk of developing a sinus infection.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking can irritate your nasal passages and increase your risk of developing sinus infections.
Key Takeaways
Sinus infections and ear infections can cause similar symptoms, but there are key differences that can help you distinguish between the two. If you are experiencing pain or discomfort in your sinuses or ears, it’s important to see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Home remedies such as rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help alleviate symptoms, but in some cases, antibiotics or other medical treatments may be necessary. By taking steps to prevent these infections, you can reduce your risk and stay healthy.